The ultimate guide to big data for businesses
Big data is the fuel for today's analytics applications. This in-depth big data guide explains how businesses can benefit from it and what they need to do to use it effectively.
The development of big data technologies unlocked a treasure trove of information for businesses. Before that, BI and analytics applications were mostly limited to structured data stored in relational databases and data warehouses -- transactions and financial records, for example. A lot of potentially valuable data that didn't fit the relational mold was left unused. No more, though.
Big data environments can be used to process, manage and analyze many different types of data. The data riches now available to organizations include customer databases and emails, internet clickstream records, log files, images, social network posts, sensor data, medical information and much more.
Companies increasingly are trying to take advantage of all that data to help drive better business strategies and decisions. In a survey of IT and business executives from 94 large companies conducted by consultancy NewVantage Partners in late 2021, 91.7% said they're increasing their investments in big data projects and other data and AI initiatives, while 92.1% reported that their organizations are getting measurable business results and outcomes from such initiatives.
However, even many of those blue-chip companies are struggling to maximize the business potential of their big data environments and analytics and AI systems. Only 39.7% of the survey respondents said they're managing data as a business asset, and just 26.5% said they've created a data-driven organization, according to a report on the annual survey that was published in January 2022.
To help companies both large and small get more value from the data flowing into their systems, this comprehensive guide to big data for businesses explains what it is, its business benefits, the challenges it poses and best practices for using it effectively. You'll also find examples of big data use cases and an overview of big data technology. Throughout the guide, there are hyperlinks to related articles that cover those topics more deeply and offer expert advice on managing big data programs.
Why is big data important for businesses?
Before big data platforms and tools were developed, many organizations could use only a small fraction of their data in operational and analytics applications. The rest often got pushed to the side as so-called dark data, which is processed and stored but not put to further use. Effective big data management processes enable businesses to better utilize their data assets.
Being able to do so expands the kinds of data analytics that companies can run and the business value they can get. Big data creates increased opportunities for machine learning, predictive analytics, data mining, streaming analytics, text mining and other data science and advanced analytics disciplines. Using those disciplines, big data analytics applications help businesses better understand customers, identify operational issues, detect fraudulent transactions and manage supply chains, among other uses.
If done well, the end results include more effective marketing and advertising campaigns, improved business processes, increased revenue, reduced costs and stronger strategic planning -- all of which can lead to better financial results and competitive advantages over business rivals. In addition, big data contributes to breakthroughs in medical diagnoses and treatments, scientific research and smart city initiatives, law enforcement and other government programs.
What are the different types of big data?
Big data encompasses a wide range of data types. While big data systems generally aren't used for transaction processing, they often store transactions, customer records, financial information, stock market data and other forms of structured data for analytics uses that go beyond the basic BI and reporting applications usually supported by conventional data warehouses.
What really distinguishes big data environments, though, is their support for unstructured and semistructured data that isn't a good fit for relational databases. Unstructured data includes text in documents, emails, survey responses, call center transcripts and social media posts, as well as images and audio and video files. Examples of semistructured data include activity logs from networks, websites, servers and mobile applications, plus data from IoT devices and industrial equipment.
The many V's of big data
Big data commonly is characterized by a set of V's, using words that begin with v to explain its attributes. Doug Laney, a former Gartner analyst who now works at consulting firm West Monroe, first defined three V's -- volume, variety and velocity -- in 2001. Many people now use an expanded list of five V's to describe big data, with these characteristics included:
- Volume. There's no minimum size level that constitutes big data, but it typically involves a large amount of data -- terabytes or more.
- Variety. As mentioned above, big data includes various data types that may be processed and stored in the same system.
- Velocity. Sets of big data often include real-time data and other information that's generated and updated at a fast pace.
- Veracity. This refers to how accurate and trustworthy different data sets are, something that needs to be assessed upfront.
- Value. Organizations also must understand the business value that sets of big data can provide to use it effectively.
Another V that's often applied to big data is variability, which refers to the multiple meanings or formats that the same data can have in different source systems. Lists with as many as 10 V's have also been created.
Big data examples and use cases
In a survey on 2022 IT spending plans conducted by Enterprise Strategy Group (ESG), TechTarget's technology analysis and research division, 56% of 196 respondents involved in data initiatives said their organizations expected to increase spending on BI, analytics and big data technologies. Another 40% said spending levels likely would be the same as in 2021, according to ESG, which published the survey results in November 2021.
The big data systems that companies deploy can be used for a variety of batch and stream processing applications, as well as interactive querying, machine learning, predictive modeling and more. Ronald Schmelzer, principal analyst and managing partner at AI research and advisory firm Cognilytica, outlined eight common use cases for big data in an article (linked to above), along with examples of them by industry. His list includes the following uses:
- getting a 360-degree view of customers to help optimize marketing, increase sales and upgrade customer service;
- improving customer acquisition and retention, which likewise is enabled by better understanding customer needs and preferences;
- strengthening fraud prevention and cybersecurity protections by better identifying suspicious transactions and security threats;
- improving business forecasts and processes, optimizing product pricing and increasing operational efficiency;
- developing personalization and recommendation systems for corporate websites, streaming services and online advertising;
- analyzing text, videos, images and audio to help understand customer sentiment, spot patterns and match content to advertising;
- enabling preventive maintenance to minimize equipment failures and downtime in manufacturing plants and other industrial operations; and
- identifying and mitigating potential risks in financial management, supply chains, logistics operations and loan and insurance policy approvals.
What are the business benefits of big data?
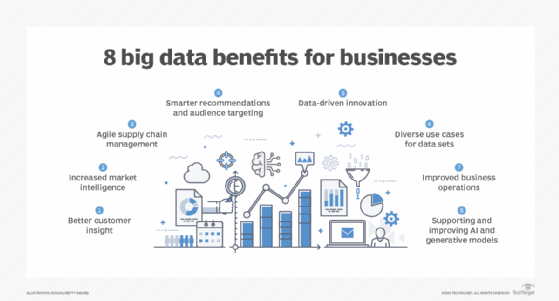
In an article on big data's business benefits, Donald Farmer, principal of analytics consultancy TreeHive Strategy, described big data as "the lifeblood of modern business." He cited the following eight potential benefits as examples of how big data systems can help organizations:
- better insight into customer preferences, buying behavior and sentiment;
- increased intelligence on market trends, products and competitors;
- agile supply chain operations that can react quickly to problems and new business needs;
- recommendation engines that are better tuned to the interests of customers;
- data-driven innovation in product development and other business functions;
- the ability to support diverse analytics use cases with the same data sets;
- operational improvements, such as lower costs and proactive equipment maintenance; and
- ensuring that data and analytics platforms can meet future business needs.
At a higher level, big data benefits companies by generating actionable insights that enable them to implement data-driven strategies and decision-making. It can also point organizations toward new business opportunities, potential cost savings and emerging market trends. In addition, real-time analytics applications fueled by big data can be used to provide up-to-date information and alerts about problems to operations managers, call center agents, sales representatives and other frontline workers.
What are common big data challenges?
Because of its very nature, big data tends to be challenging to process, manage and use effectively. Big data environments typically are complex, with multiple systems and tools that need to be well orchestrated to work smoothly together. The data itself is also complex, particularly when data sets are large and varied or involve streaming data.
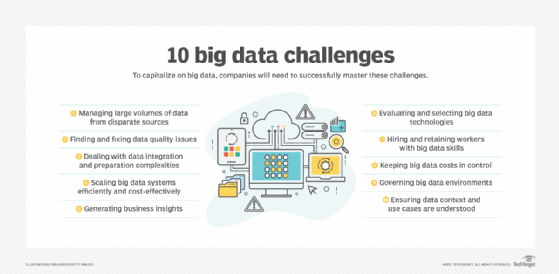
An article by technology writer George Lawton details 10 challenges of big data deployments and offers advice on how to avoid and address them. Those issues can be broken down into the following categories:
- technical challenges that include selecting the right big data tools and technologies and designing big data systems so they can be scaled as needed;
- data management challenges, from processing and storing large amounts of data to cleansing, integrating, preparing and governing them;
- analytics challenges, such as ensuring that business needs are understood and that analytics results are relevant to an organization's business strategy; and
- program management challenges that include keeping costs under control and finding workers with the required big data skills.
Hiring and retaining skilled workers can be particularly difficult because key contributors such as data scientists, data architects and big data engineers are in high demand.
Key elements of big data environments
Big data management and analytics initiatives involve various components and functions. These are some of their core aspects that need to be factored into project plans upfront.
Big data architecture. The traditional data warehouse can be incorporated into big data architectures to store structured data. More commonly, though, architectures feature data lakes, which can store different data sets in their native formats and typically are built on technologies such as Spark, Hadoop, NoSQL databases and cloud object storage services. Other architectural layers support data management and analytics processes, as explained in an article on designing big data architectures by tech writer Mary K. Pratt. A solid architecture also provides the underpinnings that data engineers need to create big data pipelines to funnel data into repositories and analytics applications.
Big data analytics. Big data systems are primarily used for analytics applications, which can range from straightforward BI and reporting to various forms of advanced analytics done by data science teams. Machine learning, in particular, has benefitted from the availability of big data -- once mostly a scientific pursuit, it's now widely used by businesses to find patterns and anomalies in large data sets. An article by Kathleen Walch, another principal analyst and managing partner at Cognilytica, further explains how big data and machine learning algorithms can be used together to make analytics more effective.
Big data collection. Before sets of big data can be processed and analyzed, they need to be collected, often from both internal systems and external data sources. That can be a complicated undertaking because of the amount of data, its variety and the number of different sources that may be involved. Data security and privacy issues add to the challenges, even more so now that businesses need to comply with GDPR, CCPA and other regulations. Read more about collecting big data and best practices for managing the process in an article by Pratt.
Big data integration and preparation. Integrating data sets is also a crucial task in big data environments, and it adds new requirements and challenges compared to traditional data integration processes. For example, the volume, variety and velocity characteristics of big data may not lend themselves to conventional extract, transform and load procedures. As a result, data management teams often must adopt new integration techniques for big data. Once data is integrated and ready for use, it needs to be prepared for analysis, a process that includes data discovery, cleansing, modeling, validation and other steps. In data lakes that store data in its raw form, data preparation is often done by data scientists or data engineers to fit the needs of individual analytics applications.
Big data governance. Effective data governance is also vital to help ensure that collections of big data are consistent and get used properly in compliance with privacy regulations and internal data standards alike. But governing big data poses new challenges for data governance managers because of the wide variety of data they often need to oversee now. Frequently done as part of data governance programs, data quality management is an important facet of big data deployments, too. And likewise, the combination of big data and data quality requires new processes for identifying and fixing errors and other quality issues.
Prepare for a big data job interview with these questions and answers.
Best practices for big data management and analytics
An enterprise big data strategy that lays out a vision, goals and guidelines is a critical starting point for organizations. In an article on developing a strategy for big data, Walch recommended the following four steps:
- Define your company's business objectives to ensure that the strategy is aligned with them.
- Identify available data sources and assess the current state of data usage in business processes.
- Identify, prioritize and document big data use cases that meet your business objectives.
- Formulate a project roadmap that includes a gap analysis of your data architecture and existing technologies, and then reprioritize the planned use cases if necessary.
Farmer suggested six big data best practices in another article. Among other things, they include focusing on business needs over technology capabilities, collecting and storing data for possible future uses, managing sets of big data in an iterative way for different analytics applications, and considering use of the cloud to ease deployments and potentially lower costs.

Big data technologies and tools
The big data era began in earnest when the Hadoop distributed processing framework was first released in 2006, providing an open source platform that could handle diverse sets of data. A broad ecosystem of supporting technologies was built up around Hadoop, including the Spark data processing engine. In addition, various NoSQL databases were developed, offering more platforms for managing and storing data that SQL-based relational databases weren't equipped to handle.
While Hadoop's built-in MapReduce processing engine has been partially eclipsed by Spark and other newer technologies, it and other Hadoop components are still used by many organizations. Overall, the technologies that now are common options for big data environments include the following categories:
- Processing engines. Examples include Spark, Hadoop MapReduce and stream processing platforms such as Flink, Kafka, Samza, Storm and Spark's Structured Streaming module.
- Storage repositories. Examples include the Hadoop Distributed File System and cloud object storage services such as Amazon Simple Storage Service and Google Cloud Storage.
- NoSQL databases. Examples include Cassandra, Couchbase, CouchDB, HBase, MarkLogic Data Hub, MongoDB, Redis and Neo4j.
- SQL query engines. Examples include Drill, Hive, Presto and Trino.
- Data lake and data warehouse platforms. Examples include Amazon Redshift, Delta Lake, Google BigQuery, Kylin and Snowflake.
- Commercial platforms and managed services. Examples include Amazon EMR, Azure HDInsight, Cloudera Data Platform and Google Cloud Dataproc.
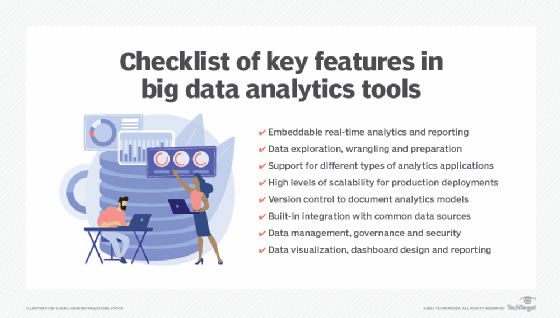
Learn about the features and capabilities of 17 open source big data tools, including many of the technologies listed above, and read a comparison of Hadoop and Spark that examines their architectures, processing capabilities, performance and other attributes. Another article details a set of useful big data analytics features to look for in tools.
What are future trends in big data?
Increasingly, organizations are running big data systems in the cloud, often using vendor-managed platforms that provide big data as a service to simplify deployments and ongoing management. As Cognilytica's Schmelzer wrote in an article about top big data trends, moving to the cloud enables businesses to "deal with almost limitless amounts of new data and pay for storage and compute capability on demand without having to maintain their own large and complex data centers."
He also listed the following as notable trends:
- increasing data diversity, driven in particular by growing data volumes from IoT devices that are leading more organizations to adopt edge computing to better handle processing workloads;
- further increases in enterprise use of machine learning and other AI technologies, both for data analytics and to enable chatbots to provide better customer support with more personalized interactions; and
- wider adoption of DataOps practices for managing data flows, as well as a heightened focus on data stewardship to help organizations deal with data governance, security and privacy issues.








