columnar database
What is a columnar database?
A columnar database (column-oriented) is a database management system (DBMS) that stores data on disk in columns instead of rows. The purpose of a columnar database is to efficiently read data from hard disk storage in order to speed up the time it takes to return a query. Columnar databases store data in a way that greatly improves disk I/O performance. They are particularly helpful for data analytics and data warehousing.
Columnar database vs. row-oriented database
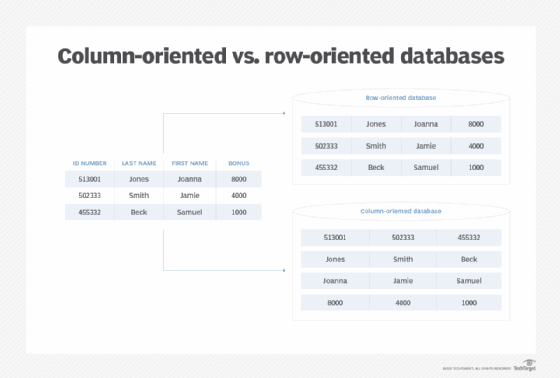
Column-oriented databases and row-oriented databases are both methods for storing data in data warehouses. They both use tables with rows containing entries and columns for the data about the entry. However, they have different approaches to how the data is stored on disk: Row-oriented databases store the data for each row together, while columnar databases store the data for each column together.
The primary limiting factor in large modern databases is not the speed of the processor, it is how fast data can be read off the disk. Many databases are terabytes of data, with some large ones reaching into the petabyte range. Databases this large are impossible to keep in any computer's random access memory (RAM), so they need to be read off the disk. Even extremely fast NVMe solid-state drives cannot keep up with the speed of processors, making the disk access the limiting factor in databases.
It is also true that sequential reads from disks are faster than random or partial reads; this is especially true for spinning platter hard drives, but also applies to solid-state storage devices. Therefore, how the data is arranged and stored on a disk will have a massive impact on the overall database performance.
The main benefit of a columnar database is faster read and query performance for analytics and big data compared to a row-oriented one. That's because most queries use column data more than row data, requiring less data to be read off a disk. Also, because the initial data retrieval is done on a column-by-column basis, only the columns that need to be used are retrieved. This makes it possible for a columnar database to scale efficiently and handle large amounts of data.
In extremely large, clustered servers and hyperconverged databases, the issue of how data is stored is compounded. A database at these scales needs to be split (sharding) between many servers, with each server only having portions of the total data. These servers are also connected through relatively slow network links. Columnar databases are well suited for scaling across several servers. Storing the same type of data together can make optimizing and finding the data easier.
The same types of operations can be performed on both row-oriented and column-oriented databases. While some may classify columnar databases as NoSQL, they can typically run SQL quires.
To understand the possible performance improvement of a columnar database versus a row-based one, imagine needing to create a pie chart based on the total sales data in a billion-row database with each row representing a single sale. In a row-oriented database, it would need to read every row to find the sale value and add it to the totals; so, it would need to read almost the entire database or perform random reads. In a columnar database, it would only need to read the sale value column which is all stored together.
Some databases use a hybrid approach. It may store the data as both column and row oriented and use a cost-based optimizer to decide which to use based on the query type. Others may store some tables by row and others by column.
Reading and writing data is much more efficient in a columnar database than a row-oriented one.
Columnar database example
In a columnar database, all the values in a column are physically grouped together on the disk. For example, all the values in column 1 are grouped together; then all values in column 2 are grouped together; etc. The data is stored in record order, so the 100th entry for column 1 and the 100th entry for column 2 belong to the same input record. This enables individual data elements, such as customer name, to be accessed in columns as a group, rather than individually row by row.
Here is an example of a simple database table with four columns and three rows.
| Account number | Last name | First name | Purchase (in dollars) |
| 0411 | Moriarty | Angela | 52.35 |
| 0412 | Richards | Jason | 325.82 |
| 0413 | Diamond | Samantha | 25.50 |
In a row-oriented DBMS, the data would be stored like this:
0411,Moriarty,Angela,52.35;0412,Richards,Jason,325.82;0413,Diamond,Samantha,25.50.
In a columnar DBMS, the data would be stored like this:
0411,0412,0413;Moriarty,Richards,Diamond;Angela,Jason,Samantha;52.35,325.82,25.50.
Note how this puts the similar data types -- integers, letters, and floats -- together. For example, calculating the average of the purchases would be easier based on the columnar example than in the row-based one.
Benefits of using a columnar database
Columnar databases have been around for decades but offer benefits for modern business applications, such as data analytics, business intelligence (BI) and data warehousing -- but that's not all. Here are four key advantages of columnar databases:
- Multipurpose. Columnar databases receive a lot of attention with big data applications. They're also used for other purposes: running online analytical processing (OLAP) cubes, storing metadata and doing real-time analytics. Columnar databases are efficient for these tasks because they excel at processing data quickly.
- Compressible data. Data can be highly compressed in a columnar database. This is because data for empty cells doesn't need to be stored at all, it is simply omitted. Also, it puts similar data -- such as all numerical data or all text -- together. This allows for advanced compression like run length compression, token dictionary/stores, or LZW compression. The compression additionally permits columnar operations -- like MIN, MAX, SUM, COUNT and AVG -- to be performed fast. Due to the high compression of columnar databases, denormalized databases can be the same storage size as a normalized relational database but with higher read performance due to the denormalization.
- Self-indexing. Another benefit of a column-based DBMS is self-indexing, which uses less disk space than a relational database management system containing the same data and several indexes.
- Speed and efficiency. Columnar databases perform analytical queries faster than other database methodologies. They are also quick and efficient at performing joins, a way of combining data from two tables in a relational database. Although it's a standard way of combining data, a join can be inefficient and slow performing. A columnar database can join any number of data sets quickly, and it can aggregate the results of a query into a single output.
Columnar database limitations
Traditional databases are more suitable for incremental data loading than columnar databases. Incremental data loading is a technique that implements a bulk data load into a database by loading only a subset of the data.
The data is loaded according to a trigger, which is a point where the data can be loaded more efficiently. An example of a trigger is when another user adds data or when a certain time of day occurs. If the trigger occurs, then the subset of data before the trigger point is loaded into the database. This technique is ideal for loading historical data or recently updated or created data.
Online transaction processing (OLTP) applications are also not suitable in column-oriented databases. Row-oriented databases work better for OLTP applications because they have better concurrent processing and isolation capabilities. Row-oriented databases can maintain ACID better than columnar ones.
OLTP is a type of DBMS that handles large amounts of data and short-term queries. Data is stored until it is modified or deleted, and the OLTP system will typically remain operational during this storage period. In contrast, OLAP system data is aggregated and analyzed to provide a strategic business view. The data storage needs of OLTP and OLAP are different. OLTP mainly performs insert, update and delete operations, while OLAP mainly reads aggregated data.
As the use of in-memory analytics increases, the relative benefits of row-oriented versus column-oriented databases may become less important. In-memory analytics is not concerned with efficiently reading and writing data to a hard disk. Instead, it allows data to be queried in RAM.
Column-oriented databases can be slow to write to, as updating a single row can require writing to multiple disks, or reordering data already written to a disk. This makes them better suited for write once, ready many (WORM) databases. Many columnar DBMSes will cache new data in a temporary row store, then write it to the columnar store during a scheduled maintenance job.
Databases are a key part of data management. Find out what you need to know to effectively manage data in today's enterprise.







