
Hadoop
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is an open source distributed processing framework that manages data processing and storage for big data applications in scalable clusters of computer servers. It's at the center of an ecosystem of big data technologies that are primarily used to support data science and advanced analytics initiatives, including predictive analytics, data mining, machine learning and deep learning.
Hadoop systems can handle various forms of structured, semistructured and unstructured data, giving users more flexibility for collecting, managing and analyzing data than relational databases and data warehouses provide. Hadoop's ability to process and store different types of data makes it a particularly good fit for big data environments. They typically involve not only large amounts of data, but also a mix of transaction data, internet clickstream records, web server and mobile application logs, social media posts, customer emails, sensor data from the internet of things (IoT) and more.
Formally known as Apache Hadoop, the technology is developed as part of an open source project within the Apache Software Foundation. Multiple vendors offer commercial Hadoop distributions, although the number of Hadoop vendors has declined because of an overcrowded market and competitive pressures driven by the increased deployment of big data systems in the cloud.
The shift to the cloud also enables users to store data in lower-cost cloud object storage services instead of Hadoop's namesake file system. As a result, Hadoop's role has been reduced in many big data architectures and the framework has been partially eclipsed by other technologies, such as the Apache Spark processing engine and the Apache Kafka event streaming platform.
How does Hadoop work for big data management and analytics?
Hadoop runs on commodity servers and can scale up to support thousands of hardware nodes. Its file system is designed to provide rapid data access across the nodes in a cluster, plus fault-tolerant capabilities so applications can continue to run if individual nodes fail. Those features helped Hadoop become a foundational data management platform for big data analytics uses after it emerged in the mid-2000s.
Because Hadoop can process and store such a wide assortment of data, it enables organizations to set up data lakes as expansive reservoirs for incoming streams of information. In a Hadoop data lake, raw data is often stored as is so data scientists and other analysts can access the full data sets, if need be; the data is then filtered and prepared by analytics or data management teams to support different applications.
Data lakes generally serve different purposes than traditional data warehouses that hold cleansed sets of transaction data. But the growing role of big data analytics in business decision-making has made effective data governance and data security processes a priority in Hadoop deployments. Hadoop can also be used in data lakehouses, a newer type of platform that combines the key features of data lakes and data warehouses, although they're more commonly built on top of cloud object storage.
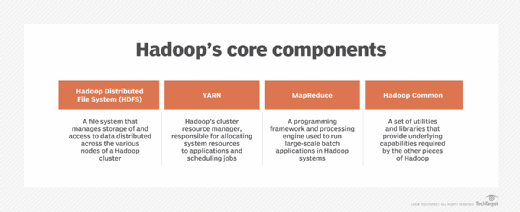
Hadoop's 4 main modules
Hadoop includes the following four modules as its primary components:
1. Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
It's the primary data storage system for Hadoop applications and also manages access to the data in clusters. HDFS is built around an architecture of NameNodes and DataNodes. Each cluster includes one NameNode, a master node that manages the file system's namespace and controls file access, plus multiple DataNodes that manage storage on the servers that make up the cluster.
2. Hadoop YARN
Short for Yet Another Resource Negotiator, but typically referred to by the acronym alone, YARN is Hadoop's cluster resource management and job scheduling technology In Hadoop clusters, YARN sits between HDFS and the processing engines deployed by users. It uses a combination of containers, application coordinators and node-level monitoring agents to dynamically allocate cluster resources to applications and oversee the execution of processing jobs. YARN supports multiple job scheduling approaches, including a first-in-first-out queue and several methods that schedule jobs based on assigned cluster resources.
3. Hadoop MapReduce
This is a built-in programming framework and processing engine for running batch applications that group together various transactions or processes. As its name indicates, MapReduce uses map and reduce functions to split processing jobs into multiple tasks that run at the cluster nodes where data is stored and then to combine what each task produces into a coherent set of results. It supports parallel processing of large data sets across Hadoop clusters in a fault-tolerant way.
4. Hadoop Common
A set of shared utilities and libraries, Hadoop Common supports the other modules by providing various cluster configuration, management and security features. Examples include a key management server, a secure mode for user authentication and access, a registry of application services running in a cluster and a service-level authorization mechanism to help ensure that clients have permission to access particular services.
Hadoop's benefits for users
Despite the emergence of alternative options, especially in the cloud, Hadoop can still benefit big data users for the following reasons:
- It can store and process vast amounts of structured, semistructured and unstructured data.
- It protects applications and data processing against hardware failures. If one node in a cluster goes down, Hadoop automatically redirects processing jobs to other nodes to ensure that applications continue to run.
- It doesn't require that data be processed before being stored. Organizations can store raw data in HDFS and decide later how to process and filter it for specific analytics uses.
- It's scalable -- companies can add more nodes to clusters when needed to handle more data or increased processing workloads.
- It can support real-time analytics applications to help drive better operational decision-making, as well as batch workloads for historical analysis.
Overall, Hadoop enables organizations to collect, store and analyze more data, which can expand analytics applications and provide information to business executives, managers and workers that they previously couldn't get.
Hadoop applications and use cases
YARN enables Hadoop users to run applications on processing engines other than MapReduce, such as Spark, Kafka, Apache Flink and Apache Storm. As a result, Hadoop clusters can handle a variety of applications in addition to batch processing jobs, including interactive querying, stream processing and real-time analytics.
For example, manufacturers, oil and gas companies, utilities and other businesses are using real-time data that's streaming from IoT devices in predictive maintenance applications to try to detect equipment failures before they occur. Fraud detection, website personalization and customer experience scoring are other use cases that involve real-time streaming and analytics.
Some other common use cases for Hadoop include the following:
- Customer analytics. Examples include efforts to predict customer churn, analyze clickstream data to better target online ads to web users and track customer sentiment based on comments about a company on social networks.
- Risk management. As part of their risk management strategies, financial services companies use Hadoop clusters to develop more accurate risk analysis models for use internally and by their customers. They've also built investment models and developed trading algorithms in Hadoop-based big data systems.
- Operational intelligence. For example, Hadoop can help telecommunications companies better understand the performance of switching systems and network utilization for capacity planning and management. By analyzing how mobile services are used and the available bandwidth in geographic regions, telcos can also determine the best places to locate new cell towers and respond more quickly to network problems.
- Supply chain management. Manufacturers, retailers and trucking companies use Hadoop systems to track the movement of goods and vehicles so they can determine the costs of various transportation options. In addition, they can analyze large amounts of historical, time-stamped location data to map out potential delays and optimize delivery routes.
Hadoop has been deployed for many other uses, too. For example, insurers use the technology for applications such as analyzing policy pricing and managing safe driver discount programs. Also, healthcare organizations look for ways to improve treatments and patient outcomes with Hadoop's aid.
Big data tools associated with Hadoop
The ecosystem that has been built up around Hadoop includes a range of other open source technologies that can complement and extend its basic capabilities. The following are some notable Apache big data tools that are related to Hadoop:
- Ambari, software that systems administrators can use to provision, manage and monitor Hadoop clusters.
- Atlas, a set of metadata management and data governance services for use in Hadoop systems.
- Flume, a tool used to collect and aggregate large amounts of streaming event data and then move it into HDFS.
- HBase, a distributed wide-column database for storing large sets of big data that's often paired with Hadoop.
- Hive, a data warehouse system and SQL query engine built on top of Hadoop that enables users to structure and analyze large data sets.
- Mahout, a distributed linear algebra framework for creating machine learning algorithms.
- Oozie, a workflow scheduling system for managing Hadoop jobs by organizing them into directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) of actions.
- Ozone, a distributed object store built on the Hadoop Distributed Data Store block storage layer and designed for use in on-premises systems.
- Phoenix, a SQL-based transaction processing and operational analytics engine that provides a relational database layer on top of HBase.
- Pig, a high-level language and software platform for developing data analysis programs that run on Hadoop clusters.
- Ranger, a data security monitoring and management framework for Hadoop environments.
- Submarine, a cloud-native machine learning platform that was initially developed as part of Hadoop and supports YARN.
- Tez, a YARN-based application framework and execution engine that uses complex DAGs to streamline processing jobs compared to MapReduce.
- ZooKeeper, a configuration, synchronization and naming registry service for large distributed systems.
Challenges in using Hadoop
Hadoop was a groundbreaking technology that made the deployment of big data environments feasible, but some limitations have complicated its use and contributed to its reduced role in organizations. The following are some of the challenges that users can face with Hadoop:
- Performance issues. The amount of data reads and writes that Hadoop needs to process on disk storage across a cluster can slow down performance. Spark has ousted MapReduce in many batch applications because its use of in-memory processing often gives it a performance advantage. Spark and Hadoop are still frequently used together, minus MapReduce, but Spark -- and other processing engines -- can also bypass HDFS and YARN to completely cut out Hadoop.
- High costs. Hadoop tightly couples compute and storage resources to streamline processing. But if either processing or storage requirements increase, more cluster nodes need to be added than might be necessary if compute and storage were separated. Disk storage with HDFS is also more expensive than cloud object storage alternatives, such as Amazon Simple Storage Service, Google Cloud Storage and Microsoft's Azure Blob Storage.
- Unused capacity. Another issue related to the coupling of compute and storage resources is the excess capacity that can result when nodes are added to a cluster. For example, a new node's processing resources might sit idle if it was primarily installed to provide more data storage capacity. That has both cost and maintenance implications.
- Management complexity. Deploying and managing large Hadoop clusters can be difficult for organizations. The need to incorporate various other big data technologies into Hadoop systems further adds to the complexity. Beyond cluster management, data management functions such as data integration and data quality can also be challenging.
- On-premises orientation. Hadoop was initially developed for on-premises deployments. While its components can now be used as part of cloud-based big data platforms, Hadoop as a whole is still primarily known as an on-premises technology.
History of Hadoop
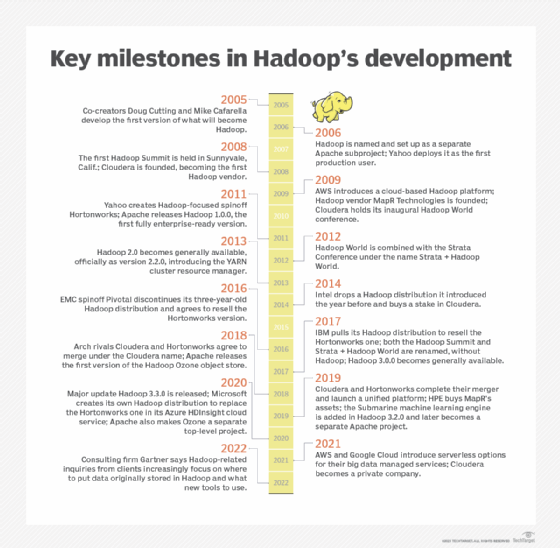
Hadoop was created by computer scientists Doug Cutting and Mike Cafarella, initially to support processing in the Nutch open source search engine and web crawler. After Google published technical papers detailing its Google File System and MapReduce programming framework in 2003 and 2004, Cutting and Cafarella modified earlier technology plans and developed a Java-based MapReduce implementation and a file system modeled on Google's.
In early 2006, those elements were split off from Nutch and became a separate Apache subproject, which Cutting named Hadoop after his son's stuffed elephant. At the same time, Cutting was hired by internet services company Yahoo, which became the first production user of Hadoop later in 2006.
Use of the framework grew over the next few years, and three independent Hadoop vendors were founded: Cloudera in 2008, MapR Technologies a year later and Hortonworks as a Yahoo spinoff in 2011. In addition, AWS launched a Hadoop cloud service in 2009. That was all before Apache released Hadoop 1.0.0, which became available in December 2011 after a succession of 0.x releases.
MapReduce, HDFS and Hadoop Common were the core components in the first iteration of Hadoop. MapReduce initially functioned as both Hadoop's processing engine and cluster resource manager, which tied HDFS directly to it and limited users to running MapReduce batch applications.
That changed in Hadoop 2.x, which became generally available in 2013 when version 2.2.0 was released. It introduced YARN, which took over the cluster resource management and job scheduling functions from MapReduce. YARN ended the strict reliance on MapReduce and opened up Hadoop to other processing engines and various applications besides batch jobs.
The Hadoop 2.x series of releases also added high availability and federation features for HDFS, support for running Hadoop clusters on Microsoft Windows servers and other capabilities designed to expand the distributed processing framework's versatility for big data management and analytics.
Subsequent releases include the following:
- Hadoop 3.0.0. The next major version of Hadoop, released by Apache in 2017, it added a YARN Federation feature that enabled YARN to support tens of thousands of nodes or more in a single cluster, up from a previous 10,000-node limit. It also included support for GPUs and erasure coding, an alternative to data replication that requires significantly less storage space.
- Hadoop 3.1.x and 3.2.x. These release series enabled Hadoop users to run YARN containers inside Docker ones and introduced a YARN service framework that functions as a container orchestration platform. The Submarine machine learning engine and Ozone object store were also added as part of them. Submarine and Ozone were initially Hadoop components but became separate top-level projects within Apache in 2019 and 2020, respectively.
- Hadoop 3.3.0. The last major release to date, it became available in 2020 with support for Arm processors, a catalog system for YARN applications and other new features. Five updates with bug fixes, improvements and enhancements were released between June 2021 and March 2023.
Evolution of the Hadoop market
In addition to AWS, Cloudera, Hortonworks and MapR, several other IT vendors -- most notably, IBM, Intel and the now-defunct Pivotal Software -- entered the Hadoop distribution market. However, the latter three companies all later dropped out after failing to make much headway with Hadoop users. Intel stopped offering its distribution and invested in Cloudera in 2014, while Pivotal and IBM exited the market and agreed to resell the Hortonworks version of Hadoop in 2016 and 2017, respectively.
Even the remaining vendors hedged their bets on Hadoop itself by expanding their big data platforms to also include Spark and numerous other technologies. In 2017, both Cloudera and Hortonworks dropped the word Hadoop from the names of rival conferences they were then putting on for big data users.
The market consolidation continued in 2019, when Cloudera acquired Hortonworks in a merger of the two former rivals and Hewlett Packard Enterprise bought the assets of MapR after the big data vendor warned that it might have to shut down if it couldn't find a buyer or new funding.
Increasingly, users and vendors alike are focused on cloud deployments of big data systems. AWS still offers its cloud service, originally called Elastic MapReduce and since renamed Amazon EMR. Organizations looking to use Hadoop and related technologies in the cloud can also turn to other managed services, including Microsoft's Azure HDInsight and Google Cloud's Dataproc.
Despite its name, Cloudera still got about 90% of its revenue from on-premises deployments as of September 2019. To try to remain competitive, it launched a new cloud-native platform that month. Cloudera Data Platform (CDP) combines elements of the separate Cloudera and Hortonworks distributions and supports multi-cloud environments. Cloudera has since said that Hadoop is just one of many technologies included in CDP and accounts for only a small part of its business now.
The development of CDP prompted Microsoft to create its own Hadoop distribution for Azure HDInsight, which previously was based on the Hortonworks one. Microsoft's version, which was released in 2020 and also includes a Spark implementation, is essentially a clone of the Hortonworks technology. Notable moves in the market since then include AWS and Google both introducing serverless options for their big data platforms in 2021 and Cloudera becoming a private company that year through a $5.3 billion buyout by two investment firms. Overall, though, Hadoop development by vendors has slowed down.
In a May 2022 blog post, Merv Adrian, then an analyst at Gartner, said Hadoop-related inquiries from the consulting firm's clients had dropped sharply over the past 25 months. Adrian, who is now an independent analyst, also said the inquiries being submitted were "increasingly about where to put the data first assembled for use with the original Hadoop tool set, and what new tools to use." Hadoop "is far from dead," he wrote, but more and more for big data users, "it's not about Hadoop anymore -- it's about what's next."







